E.ON Texas wind battery gains point to expanding storage openings
E.ON has used falling battery prices and supply chain learnings to lower the cost of its Texas Waves projects as market-driven applications spur storage sector growth, Mark Frigo, E.ON Vice President, Head of Energy Storage, North America, told New Energy Update.

Related Articles
Last month, E.ON started building the 20 MW Texas Waves energy storage projects, consisting of two 10 MW lithium ion energy storage systems at the operational Pyron and Inadale windfarms in West Texas.
The Texas Waves projects will use LG Chem battery systems to provide frequency response services to the network operator Electric Reliability Council of Texas (ERCOT). The storage plant will allow E.ON to bid into the Fast Responding Regulation Service Up and Down (FRRS) market any time of day, responding to events such as a large generator trip.
The Texas Waves projects highlight the growing commercial opportunities for energy storage projects to supplement rising renewable energy capacity. The project economics benefit from an Investment Tax Credit (ITC), but energy storage battery and balance of system costs are falling fast.
EON has already used learnings from its 10 MW Iron Horse solar plus storage facility- completed in April- to cut the costs for the Texas Waves projects, Frigo said.
"We had learnings across the board, ranging from commercial to technical," he said.
A key driver of cost reductions was the “right sizing” of the battery, Frigo said.
E.ON drew from LG Chem's experience in frequency regulation applications to optimize the battery size to minimize the storage life-cycle costs, he said.
Texas Waves will also use a Greensmith software control system, which interacts directly with the battery, the power conversion system and the battery management system, to help increase operational efficiency and maximize the battery life, Frigo noted.
E.ON's other learnings include a better understanding of energy storage supply chain companies and services, and increasing knowledge of the detailed design features of battery projects and sub-metering requirements, he said.
Demand driven
Growth in energy storage projects is being driven by a combination of system need and niche behind the meter commercial opportunities, rather than clear market regulation, Aris Karcanias, Co-lead Global Clean Energy Practice at FTI, Consulting, told New Energy Update.
In renewable energy applications, energy storage developers are looking to improve local grid stability, address curtailment, and deal with the misalignment between production centres and load centres, he said.
"The business models are often very case specific...it will be very much reliant on the source of revenue and the type of problem that is sought to be addressed," he said.
Deepwater Wind’s "Revolution Wind" offshore project is a good example of market-driven storage opportunities, Karcanias said.
Deepwater is proposing to build a 144 MW wind farm in Massachusetts waters paired with a 40 MWh Tesla battery storage system, following a Request for Proposals (RfP) for low carbon generation by local municipalities. The projects must be able to deliver power to customers in winter afternoons and evenings.
The Revolution Wind proposal shows energy storage can maximize power value through energy arbitrage, Karcanias said.
"It's the misalignment between demand and supply patterns which have enabled a commercial solution to be viable," he said.
This model could be transferred to other onshore wind markets, Karcanias said.
"Wherever you have a need for the time shift in production to match peak periods demand, you will start to see these types of models emerging," he said.
Responsive rules
Business models for renewable energy storage will continue to improve as wind and solar capacity replaces dispatchable conventional generation and operators create marketplaces for energy storage supply.
In many states, wind power has become more competitive than fossil fuel plants, fuelling further demand for wind projects and increasing the need for solutions to mitigate intermittency.
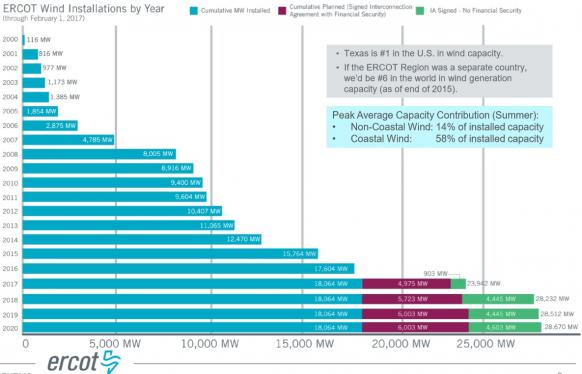
Texas wind growth forecast
(Click image to enlarge)
Source: ERCOT, February 2017.
An increasing number of states are implementing market mechanisms that accommodate energy storage projects and these mechanisms must take into account the evolving solutions that energy storage capacity provides, Frigo said.
In Texas, for example the FRRS frequency response market has a cap of 65 MW for regulation up and 35 MW for regulation down.
"This limits the viability for energy storage in ERCOT, which is an increasingly needed service due to the continued large amounts of wind generation being built," Frigo said.
"ERCOT is considering a new market, called Fast Frequency Regulation 1 (FFR), which would increase the amount of energy storage that can be built in ERCOT at low cost," he said.
Federal boost
Federal and state authorities are also introducing legislation to support greater participation of energy storage.
Key rulemaking efforts include Federal Energy Regulatory Commission's (FERC's) 2016 notice of proposed rulemaking requiring Regional Transmission Operators and Independent Service Operators to accommodate energy storage projects, Donna Bobbish, Counsel in Shearman & Sterling LLP’s Project Development & Finance Group, told New Energy Update.
The proposed requirements include bidding parameters that take into account energy storage characteristics. FERC's jurisdiction includes all of the main U.S. network operators except Texas's ERCOT.
The FERC is likely to issue a final rule on the proposed rulemaking in 2018, as the commission is currently working through a backlog of matters following a six-month period without a quorum earlier this year, Bobbish said.
"We should be seeing something within the next six months or so," she said.
In parallel, President Trump's administration is advancing new initiatives to improve grid stability and market pricing mechanisms in the light of rising renewable energy capacity and low gas prices.
In a new Electricity Market and Reliability report commissioned by Energy Secretary Rick Perry, the Department of Energy (DOE) called for accelerated implementation of Essential Reliability Services (ERS) mechanisms to create "fuel-neutral markets and/or regulatory mechanisms that compensate grid participants for services that are necessary to support reliable grid operations."
In order to ensure sufficient grid reliability, the DOE called for "a mix of market approaches, technology enhancements, and reliability rules or other regulatory rule changes," reiterating previous comments by the North American Electric Reliability Corporation (NERC).
While rulemakers move towards greater integration of storage technologies, supply-side innovations will continue to drive down costs and provide a wider range of opportunities.
"There are many energy storage opportunities in the United States that we are excited about," Frigo said.
"Most of the current opportunities are with grid support type of services, such as frequency regulation. But as costs continue to decline, we see opportunities with longer-duration applications such as solar shifting, peaking, and transmission and distribution deferral," he said.
New Energy Update